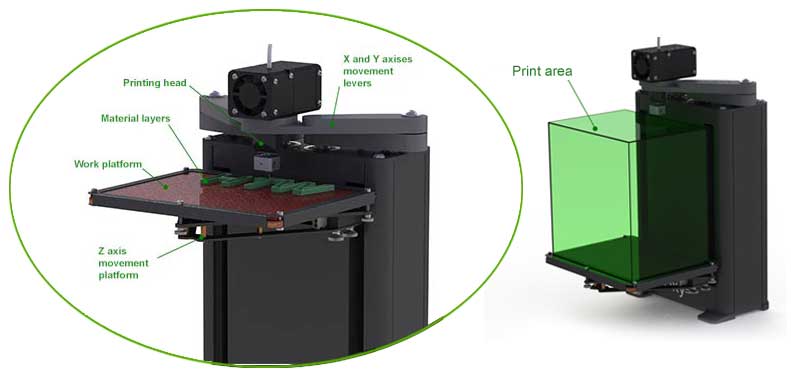
Printing process on a 3D printer
3D printer builds objects from a virtual 3D models. That is the future object is created first on a computer using a special 3D modeling software (3D Max, Solid Works, Maya, Blender and other). Then the 3D model is processed by program, which generates G-codes (as an example, Repetier Host). G-codes specify the trajectory and motion parameters for the printing head - separately for every layer.
The object construction is carried out by movement of the printing head in a horizontal plane along axises X and Y and material deposition layer by layer. The first layer is placed on a work table surface of the 3D printer (it is also called 3D printer bed or 3D printer surface). After the first layer is finished it is performed the movemend along Z axis for a value of the one layer thickness. Then above the next layer is placed. The printing process is repeated until the whole object will be constructed.
The thickness of the layer is critical important. The less layer thikness - the less visible is the layer-to-layer transfer, the less roughness of the surface and the more detailed can be created the object. The more layer thickhess - the simpler model can be printed. If the layer thikness is big, the printing time is less. So before the printing process it is necessary to choose suitable size of the nozzle and find a compromise between the printing speed and ready printed object quality.
Usually 3D printers allow using of different replaceable printing heads with different nozzle diameters. The minimum layer thickness, which could be achieve on a 3D printer, is called resolution of a 3D printer. The higher resolution - the higher quality, smoother and more detailed objects could be printed. But the printing resolution depends not only on a 3D printer, but also it depends on a choosed filament and settings of using software.
Besides the printing resolution the important characteristic of 3D printers is its working area - this is the zone, where it is possible to print an object. The maximum possible size of built on 3D printer object depends on the dimensions of its working table and height of Z axis possible displacement during the printing process.
If a 3D model is complex or has high-curvature part shape, special supports are needed for the printing process. A 3D printer can not fix material in the air. During the printing process the printing head lays the material on the horizontal supporting surface - working table of the printer, or on the previous layer of the material. In case the model consists of several separate parts or if some parts of the model override the limits of the lower layer, it is needed to create supporting constructions. This supports shold be removed from the ready object after the printing is finished.
Often the ready model after the printing is posting processed, support constructions are moved away, rough edges should be removed, the object is grinded and polished or chemical treated, it could be coloured. But in the most cases such processing is minimal.